Bone grafting
After a dental extraction, the tooth socket will naturally fill with bone over 3 months, however after a prolonged period of time, the bone will begin to resorb again if there is no functional replacement.
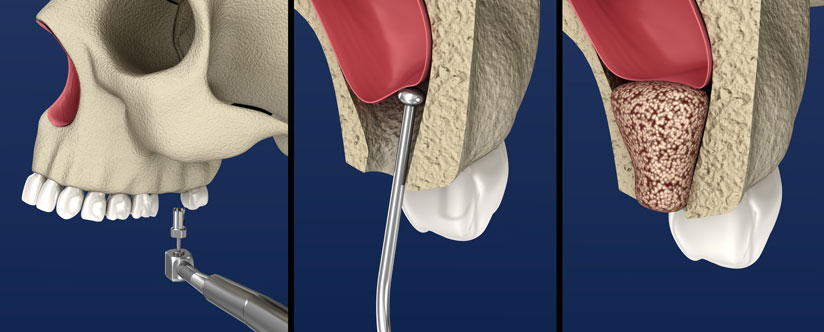
Bone grafting can be performed at the time of dental extraction to minimise the amount of bone loss (socket preservation). If the tooth has already been removed, then a scan will be taken to determine the amount of bone quantity and quality present. If there is not enough bony support for an implant, a bone grafting procedure may be required to graft new bone to the existing ridge to create a good solid bony platform for the implant. Bone grafting is usually a comfortable procedure performed under intravenous sedation. Different options are available for bone grafting materials including xenografts (different species), allografts (same species) or autografts (own bone).
A sinus lift procedure is a specific bone grafting procedure to improve the bone quantity in the posterior upper jaw, where bone is often very limited. It involved identifying the sinus membrane, elevating it and adding bone underneath the membrane to increase bone height. This ensures adequate bone support for an implant in the posterior upper jaw.